We had a group project meeting in which we created the following paragraphs together:
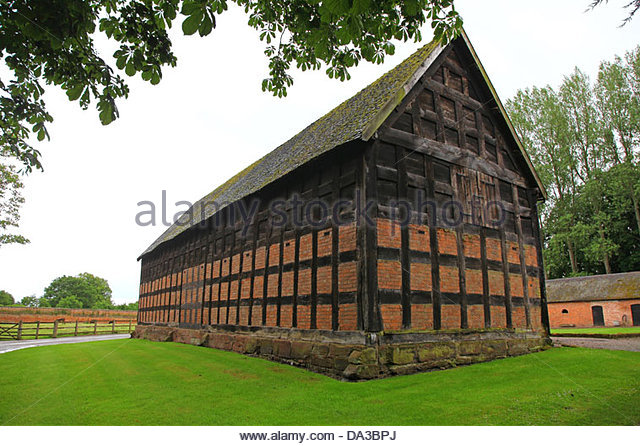
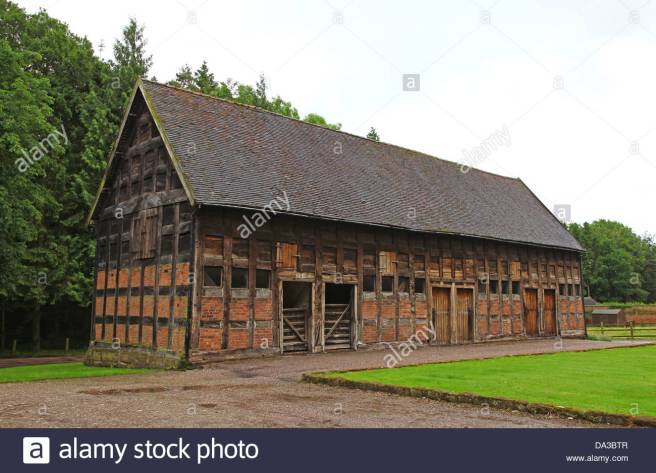
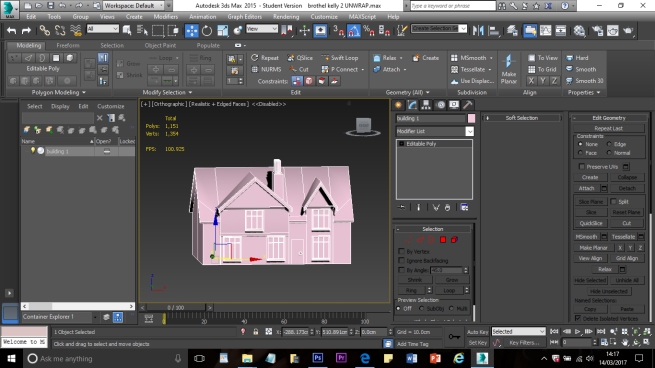
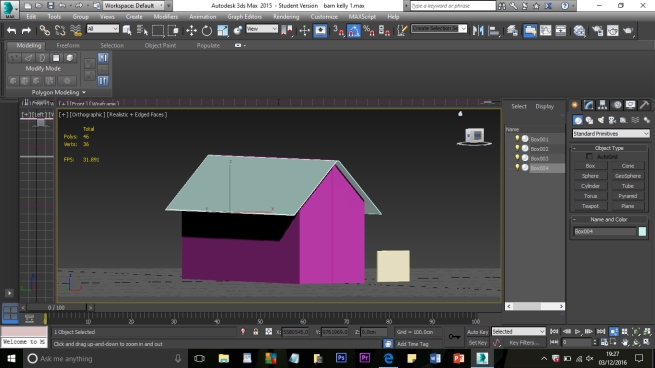
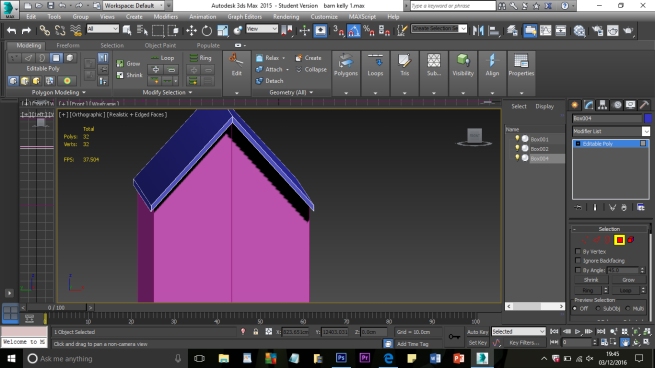
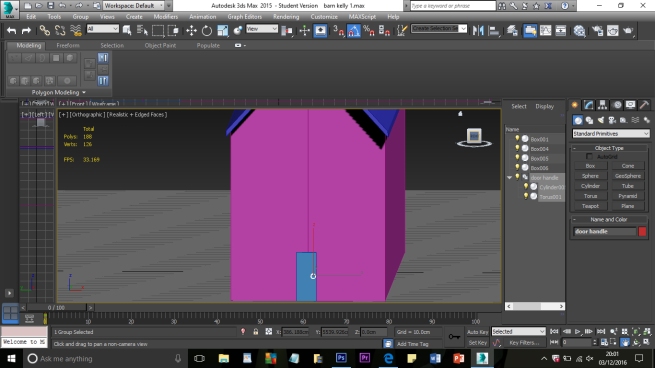
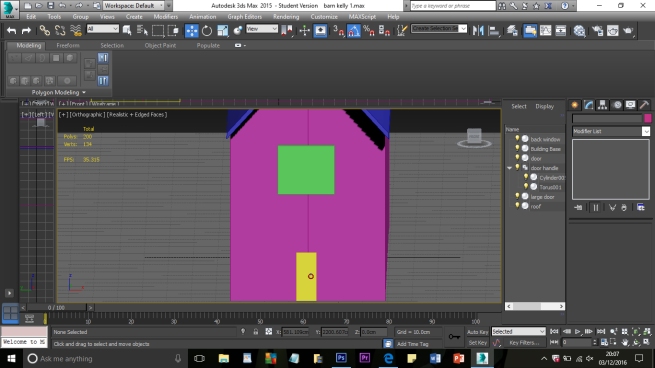
The aim of the project is to create a three-dimensional historical environment, centred around the Beverley Gate entrance to the city of Kingston Upon Hull, in April of the year 1642. The project is designed to showcase an interpretation of what the area immediately around the entrance would have looked like on the market day, several days before King Charles II attempted to enter the city, and was refused by Sir John Hotham. The environment is set around midday in order to demonstrate the hustle and bustle of the city on market day and to show some of the city’s preparations for its defence. We have a few various buildings in the level including market stalls, tavern, two blacksmiths, stables, brothel, bakery, butchers, tanners, guild hall, tailor, farm house and barn; as well as Beverley Gate itself and the city’s wall. We have used historical references where possible to re-create an accurate depiction of Beverley gate and the surrounding area. However creative license has been utilised due to the unfortunate lack of accurate physical evidence.
The environment will be created to be interactive, and will play as a game level. The environment will include a hidden object game where the player has to explore the environment in order to collect all of the objects, which reside on a list in the corner of the screen.
Ideally, we would like to present the project to the public using a combination of: pre-rendered video, virtual reality/360 degree video, and augmented reality. The pre-rendered video would be a fly through of the completed environment, as including the hardware to be able to utilise the environments interactive features would be impractical in a public space. The video will play on a computer monitor. We would also like to be able to render to video in 360 degree 3D, and use a QR code to allow people to download an app and watch it using a mobile VR headset like the Google Cardboard. We could also place the video on YouTube 360. We would like to use Augmented Reality to create an assembly game, where the user is required to physically interact with cards on a table top to recreate the environment as we have created it in the video. At minimum, we would like to be able to create the Pre-rendered video and the 360 VR video. Our intention is to engage, inform and inspire in the year of city of culture. We wish to demonstrate to the public, both local and tourists, the city’s heritage, allowing them to connect with a part of history that is usually not widely seen by or known by the general populace.